Natural gas stocks ETF investments offer direct exposure to one of America’s most volatile energy sectors. These funds track companies involved in natural gas exploration, production, and distribution.
We at Natural Resource Stocks have analyzed the top-performing natural gas ETFs and their risk profiles. This guide covers the essential strategies you need to build a profitable natural gas portfolio.
How Do Natural Gas ETFs Actually Work
Natural gas ETFs operate through two distinct mechanisms that determine your investment returns. Commodity-focused ETFs like the United States Natural Gas Fund track natural gas prices directly through futures contracts, while equity-focused funds invest in companies that operate across the natural gas value chain.
The United States Natural Gas Fund holds futures contracts that expire within one month and trades on NYMEX, with a management fee of 0.60% and total expense ratio of 1.06% (as of September 2023). This structure exposes investors to contango risk when new futures contracts cost more than expiring ones, which explains why UNG delivered a devastating -99.98% return over five years according to WisdomTree data.
Stock-Based Natural Gas ETFs Outperform Commodity Funds
The First Trust Natural Gas ETF takes a different approach and invests in natural gas exploration and production companies with an expense ratio of 0.57%. This equity-based strategy historically outperforms commodity ETFs because it captures company growth rather than just price movements.
Stock-based funds benefit from operational improvements, technological advances, and strategic acquisitions that commodity funds miss entirely. Companies like Cheniere Energy and Kinder Morgan generate revenue from long-term contracts and infrastructure assets, which provide more stable returns than volatile spot prices. The EIA reports natural gas accounts for 38% of US electricity production, which creates sustained demand that benefits equity holders more than futures traders.
Performance Metrics That Matter Most
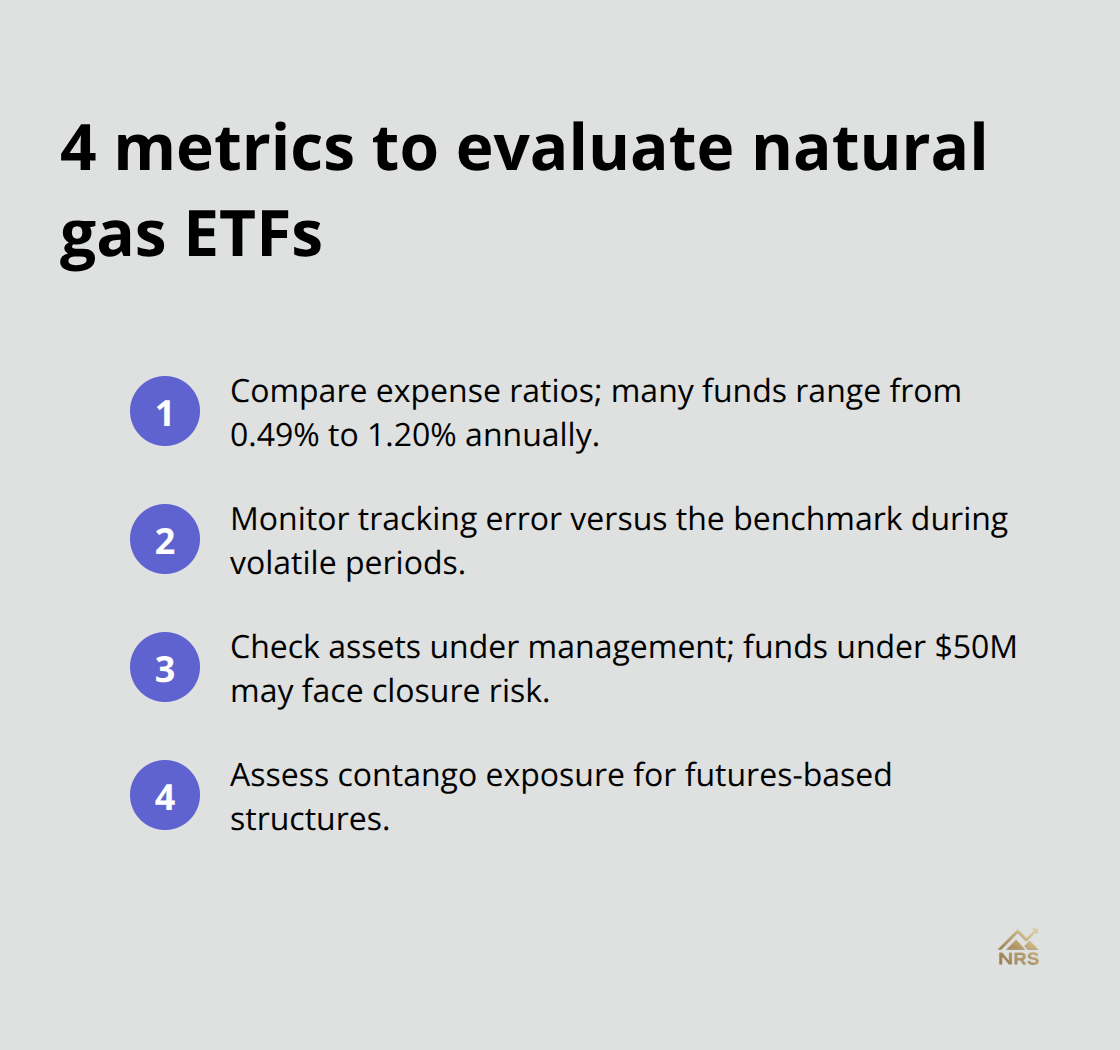
Track the expense ratio first because fees compound over time and natural gas ETFs range from 0.49% to 1.20% annually. Monitor the fund’s error rate against its benchmark since high volatility can create significant performance gaps. Assets under management indicate liquidity, with funds below $50 million that face potential closure risk.
Most importantly, examine the fund’s contango exposure if it holds futures contracts because this hidden cost destroys long-term returns systematically. These performance factors will help you identify which natural gas ETFs align with your investment strategy and risk tolerance.
Which Natural Gas ETFs Deliver Results
The United States Natural Gas Fund remains the largest natural gas ETF with $265 million in assets under management, but its futures-based strategy makes it unsuitable for long-term investors. UNG tracks Henry Hub natural gas prices through one-month futures contracts, which creates severe contango drag that destroyed 99.98% of investor capital over five years according to WisdomTree performance data. The fund charges a 0.60% management fee plus additional costs that push the total expense ratio to 1.06%.
United States Natural Gas Fund Shows Poor Long-Term Performance
UNG’s structure exposes investors to systematic value destruction through contango effects. When futures contracts expire, the fund must purchase new contracts at higher prices, which erodes returns over time. This mechanism explains why natural gas prices increased nearly 70% from March to June 2024 while UNG failed to capture these gains effectively. The fund works better for short-term traders who can exit positions before contango effects compound, but retail investors typically hold positions too long and suffer massive losses.
First Trust Natural Gas ETF Beats Commodity Funds
The First Trust Natural Gas ETF takes the superior approach and invests in natural gas companies rather than futures contracts. FCG holds stocks like EQT Corporation, Chesapeake Energy, and Range Resources that generate revenue from actual gas production and reserves. This equity-based strategy delivered positive returns during periods when UNG collapsed because companies adapt to market conditions through operational improvements and strategic acquisitions. FCG charges a reasonable 0.57% expense ratio and provides exposure to companies that benefit from projected 2.5% annual natural gas demand growth through 2027.
VanEck Oil Services ETF Captures Infrastructure Growth
The VanEck Oil Services ETF offers indirect natural gas exposure through companies that provide services to gas producers. OIH holds Schlumberger, Halliburton, and Baker Hughes that profit from increased activity regardless of commodity price fluctuations. This services-focused approach generated superior risk-adjusted returns because these companies earn fees from long-term contracts rather than depend on volatile spot prices. The fund benefits from massive infrastructure buildout required to transport natural gas from production sites to LNG export terminals (with pipeline capacity projected to increase from 8 to 12 billion cubic feet per day by 2028).
These performance differences highlight why your investment strategy matters more than market timing when you select natural gas ETFs.
How to Time Natural Gas ETF Investments
Dollar-Cost Averaging Beats Market Timing
Dollar-cost averaging works exceptionally well for natural gas ETF investments because these funds experience extreme volatility that makes timing nearly impossible. Henry Hub prices swung from under $2 in 2020 to peaks around $10 in 2005, which created massive opportunities for investors who buy consistently rather than chase price movements. The First Trust Natural Gas ETF dropped 40% during March 2020 market panic, then recovered 85% over the next 12 months. This pattern demonstrates why consistent monthly purchases capture dramatic swings better than lump-sum investments.
Set up automatic monthly purchases of $500-1000 in FCG rather than try to predict price bottoms because natural gas markets react to weather patterns, geopolitical events, and supply disruptions that professionals struggle to forecast. This systematic approach reduces your average cost per share over time and eliminates emotional decisions that destroy returns. The EIA reports that natural gas storage deficits will grow through 2026, which supports a multi-year accumulation strategy through dollar-cost averaging.
Winter Demand Drives Seasonal Price Patterns
Natural gas consumption follows predictable seasonal patterns that create profitable opportunities for active investors. Residential heating demand peaks during December through February, while summer air conditioning loads create secondary demand spikes during July and August heat waves. Weather patterns significantly influence prices, with colder winters and warmer summers that lead to consumption increases and boost natural gas company revenues and stock prices.
Start to accumulate positions in natural gas ETFs during September and October before heating season begins, then reduce exposure during April and May when demand typically drops. This seasonal rotation strategy works because utilities stockpile natural gas supplies during low-demand periods, which creates predictable inventory cycles. Global LNG demand grew 3% year-over-year in 2024 with Asia accounting for 60% of increased consumption, which adds international demand that reinforces these seasonal patterns.
Risk Management Through Position Limits
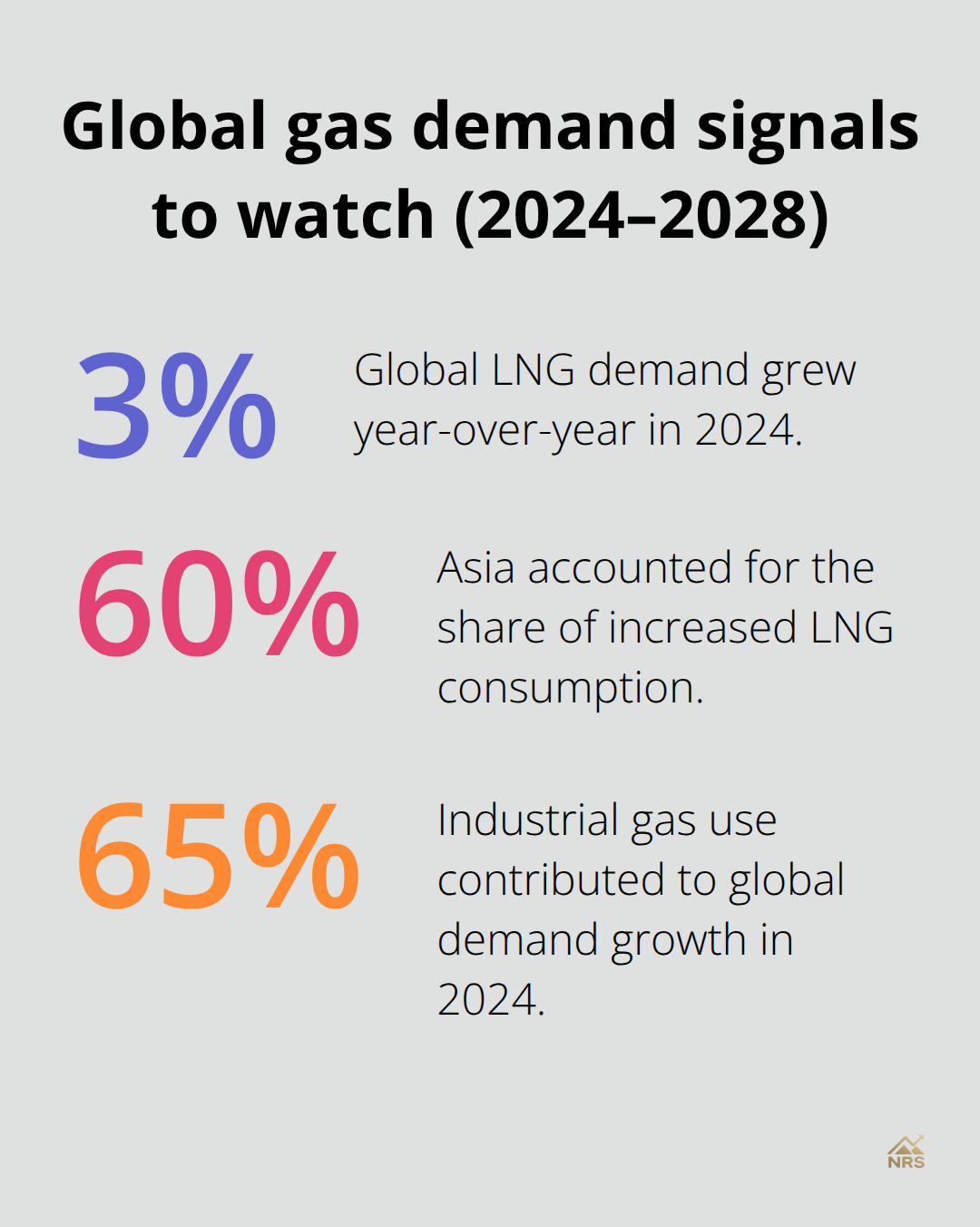
Limit natural gas ETF exposure to 5-8% of your total portfolio because commodity-linked investments experience higher volatility than broad market indices. Natural gas prices correlate with economic cycles but move independently from stock and bond markets (which provides diversification benefits when properly sized). Industrial gas use contributed 65% of global demand growth in 2024, driven by economic expansion in Asian markets, but this industrial demand creates cyclical risks that require careful position management.
Split your natural gas allocation between equity-focused ETFs like FCG and infrastructure plays like pipeline companies to reduce commodity price sensitivity. Pipeline operators like Kinder Morgan generate fee-based revenues from long-term contracts that provide stability during price downturns. This balanced approach captures natural gas sector growth while limits downside risk from volatile spot prices and maintains portfolio stability during market turbulence. Consider hedging strategies to protect your positions during volatile periods.
Final Thoughts
Natural gas stocks ETF investments provide exposure to America’s energy transition through two distinct approaches. Equity-focused funds like the First Trust Natural Gas ETF deliver superior long-term returns because they invest in companies that benefit from operational improvements and infrastructure growth. Commodity-based ETFs like UNG face systematic value destruction through contango effects that make them unsuitable for buy-and-hold investors.
You should monitor three critical factors before you invest: expense ratios that range from 0.57% to 1.06%, fund structure that determines contango exposure, and seasonal demand patterns that create predictable price cycles. Dollar-cost averaging works exceptionally well for natural gas stocks ETF investments because extreme volatility makes market timing nearly impossible. You should limit natural gas exposure to 5-8% of your portfolio and combine equity ETFs with pipeline infrastructure plays to reduce commodity price sensitivity.
Global demand growth of 2.5% annually through 2027 supports long-term accumulation strategies, while winter heating seasons create tactical opportunities for active traders. We at Natural Resource Stocks provide expert analysis and market insights to help you navigate energy sector investments (including comprehensive video content and macroeconomic analysis). Visit Natural Resource Stocks for detailed coverage of metals and energy markets that empowers your investment decisions across natural resource sectors.