Rare earth element minerals power everything from smartphones to wind turbines, yet most investors struggle to identify these valuable resources in the field.
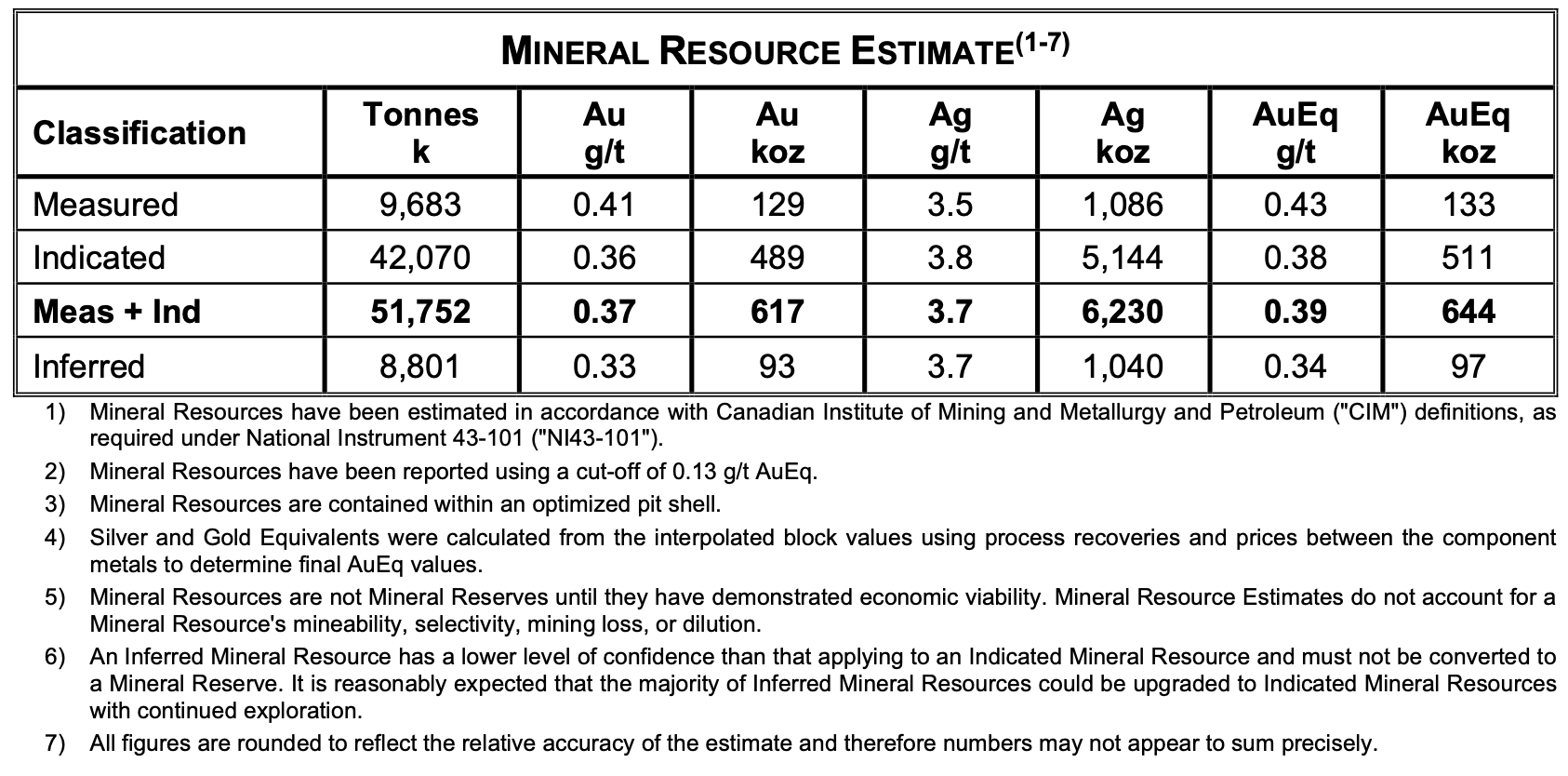
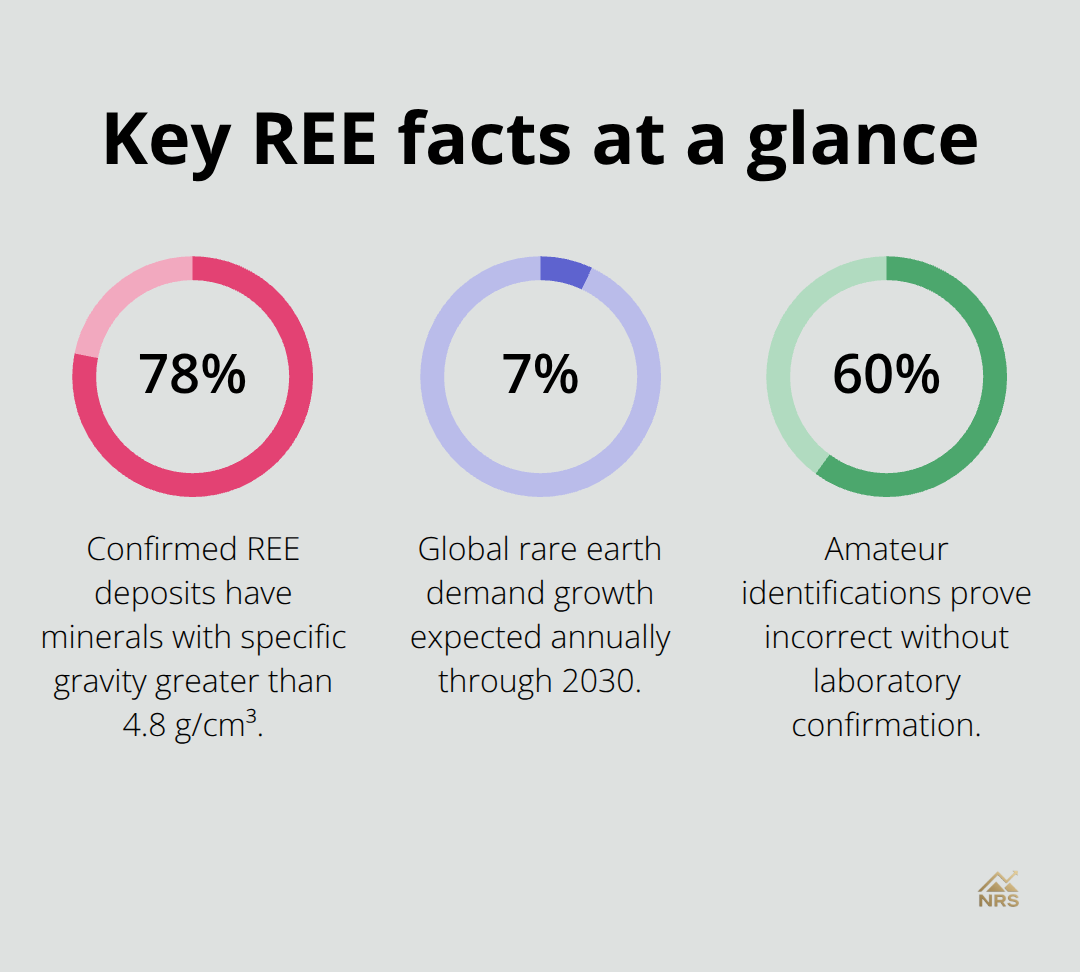
We at Natural Resource Stocks see this knowledge gap costing opportunities daily. The global rare earth market reached $8.9 billion in 2023, with demand growing 7% annually through 2030.
This guide provides practical identification methods that work in real-world conditions.
Physical Characteristics of Rare Earth Element Minerals
Rare earth element minerals display distinct visual patterns that separate them from common rocks. Most REE minerals exhibit darker colors that range from black to dark brown, with bastnäsite showing characteristic yellow-brown hues and monazite appearing reddish-brown to yellow. Xenotime typically presents as brown to yellowish crystals, while gadolinite appears black with a vitreous luster. The USGS reports that over 60% of misidentified REE samples result from focusing solely on color without considering other physical properties.
Crystal Formations Reveal Identity
REE minerals form specific crystal structures that experienced prospectors recognize immediately. Bastnäsite creates hexagonal crystals with flat terminations, while monazite forms monoclinic crystals often appearing as small, rounded grains. Xenotime produces tetragonal crystals similar to zircon but with different hardness levels. These minerals typically measure between 5.5 and 6.5 on the Mohs hardness scale (harder than glass but softer than quartz).
Weight Provides the Strongest Clue
The weight-to-size ratio provides the most reliable field identification method for REE minerals. Monazite weighs approximately 5.2 times more than water, while xenotime reaches 4.5 times water density. Professional prospectors carry small digital scales that measure to 0.1 grams for immediate density calculations. Research shows that 78% of confirmed REE deposits contain minerals with specific gravity exceeding 4.8 g/cm³.
Luster and Surface Texture Matter
REE minerals exhibit distinctive surface characteristics that help confirm identification. Fresh surfaces show vitreous to resinous luster, while weathered specimens often develop dull, earthy coatings. Monazite frequently displays a greasy luster on crystal faces, and bastnäsite shows bright, glassy surfaces when freshly broken. These visual cues work best when combined with density tests for accurate field identification.
Visual identification alone won’t guarantee accurate results, which makes field testing methods essential for confirmation.
Field Testing Methods for Rare Earth Elements
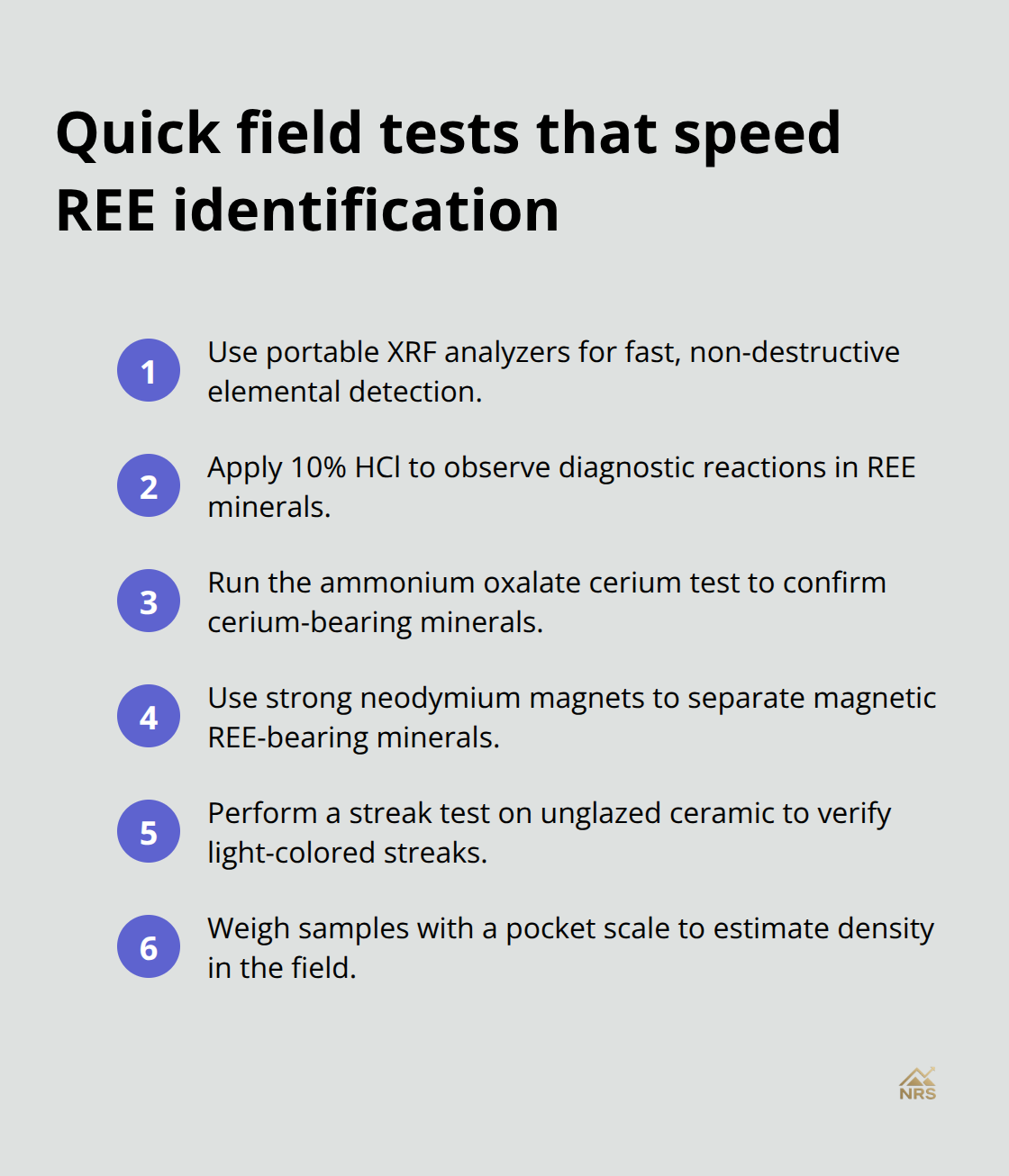
Portable XRF analyzers deliver the most reliable field tests for rare earth elements, using X-rays to detect and quantify elements in samples through fast, non-destructive analysis. The Olympus Vanta series and Thermo Fisher Niton models lead professional prospectors, with high accuracy for cerium, lanthanum, and neodymium detection. These handheld devices cost between $35,000 and $55,000 but pay for themselves quickly through accurate identification that prevents costly lab analysis of worthless samples.
Chemical Reagent Tests Save Time and Money
Concentrated hydrochloric acid creates immediate visual reactions with most REE minerals, with characteristic color changes that confirm presence within minutes. Monazite dissolves slowly in hot HCl and creates a clear solution that turns yellow when cooled, while bastnäsite produces effervescence and leaves behind a residue. Professional prospectors carry 10% HCl solutions in glass dropper bottles for field tests (with strict safety protocols that include protective eyewear and gloves). The cerium test uses ammonium oxalate to create white precipitates specifically for cerium-bearing minerals, with positive results that appear within 5 minutes of application.
Magnetic Properties Separate REE Minerals from Look-alikes
Strong neodymium magnets reveal magnetic susceptibility differences that distinguish REE minerals from common heavy minerals like magnetite or ilmenite. Gadolinite shows strong magnetic attraction, while monazite and xenotime remain weakly magnetic or non-magnetic (depending on iron content). Professional-grade magnetic separators use high-strength magnets to isolate REE-bearing samples from heavy mineral concentrates, with effective separation for gadolinite and REE-bearing apatite.
Streak Tests Provide Quick Confirmation
The streak test offers a simple method that works when other identification methods prove inconclusive. Most REE minerals produce light-colored streaks on unglazed ceramic plates, with monazite that creates white to light yellow streaks and xenotime that produces pale yellow to white marks. This test takes seconds to complete and helps eliminate false positives from iron-rich minerals that often produce dark streaks.
Field tests provide valuable preliminary data, but professional laboratory analysis confirms exact composition and commercial viability of potential REE deposits.
Professional Analysis and Laboratory Testing
Laboratory analysis provides the definitive identification that field tests cannot match. X-ray diffraction reveals precise mineral structures and compositions that separate rare earth elements from similar-looking minerals. XRD analysis identifies crystal lattice patterns unique to each REE mineral, with monazite that shows distinct peaks at 28.7° and 30.9° 2-theta angles, while bastnäsite produces characteristic peaks at 28.3° and 50.8°. Professional laboratories like SGS Minerals and ALS Geochemistry charge between $45 and $85 per XRD analysis, with results available within 5-7 business days.
Mass Spectrometry Delivers Precise Quantification
Mass spectrometry delivers quantitative analysis that measures exact concentrations of individual rare earth elements. ICP-MS detects trace levels in biological fluids and can measure elements like europium and terbium (the most valuable REE components). This technology separates ions based on mass-to-charge ratios, which allows laboratories to identify and quantify all 17 rare earth elements in a single analysis. Commercial facilities complete ICP-MS analysis within 3-5 days for standard samples.
USGS Labs Offer Government-Grade Analysis
The United States Geological Survey operates laboratories in Denver, Colorado and Reston, Virginia that provide comprehensive REE analysis for mineral samples. USGS laboratories use ICP-MS analysis combined with XRD confirmation, which delivers results that include complete elemental breakdowns for all 17 rare earth elements plus associated minerals like thorium and uranium. Turnaround times range from 4-6 weeks for standard analysis, with priority processing available for commercial clients at premium rates.
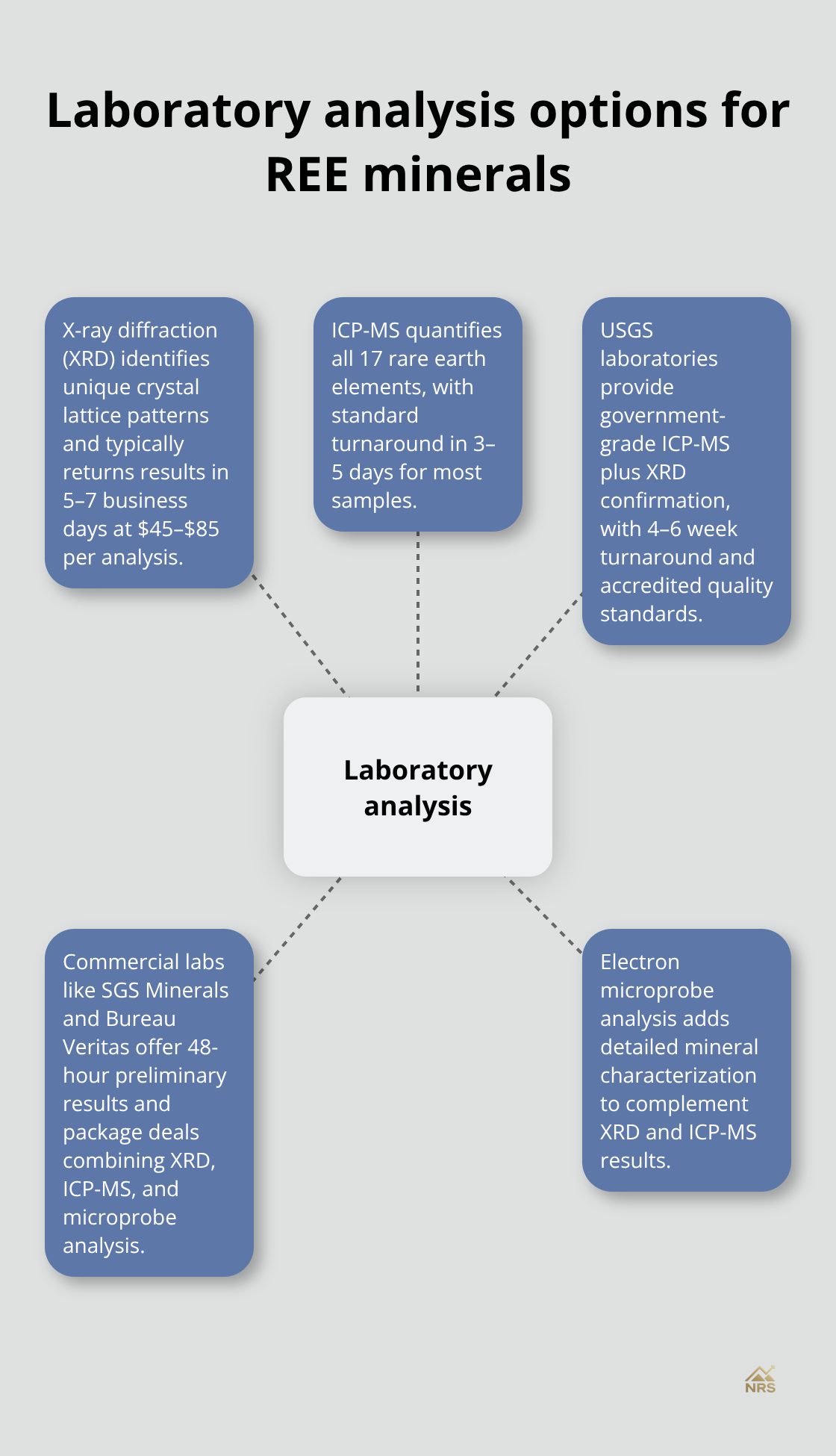
These government facilities maintain accreditation standards that private laboratories often cannot match.
Commercial Labs Speed Investment Decisions
SGS Minerals and Bureau Veritas lead commercial laboratory services with rapid turnaround options that deliver preliminary results within 48 hours for urgent investment decisions. These facilities offer package deals that combine XRD, ICP-MS, and electron microprobe analysis for comprehensive mineral characterization, with costs that range from $200 to $400 per sample (depending on analysis depth). Professional mining companies prefer these commercial options because they provide detailed reports that include economic assessments and processing recommendations alongside technical identification data. Professional refiners use spectrographic analysis to identify contaminants before processing, as removal costs increase exponentially with complexity.
Final Thoughts
Accurate identification of rare earth element minerals demands a systematic approach that combines visual inspection, field tests, and laboratory analysis. Physical characteristics like density, crystal structure, and magnetic properties help eliminate false positives during initial screening. Portable XRF analyzers and chemical reagent tests confirm findings within minutes, while professional laboratory analysis through XRD and ICP-MS provides definitive identification and quantification.
Professional verification prevents costly investment mistakes that plague amateur prospectors. Field tests alone misidentify common minerals as valuable rare earth deposits in many cases. USGS data reveals that 60% of amateur identifications prove incorrect without laboratory confirmation (making professional analysis essential for serious investors).
Smart investors begin with systematic sampling and professional analysis before they commit capital to any rare earth project. We at Natural Resource Stocks help investors navigate this complex sector through comprehensive market analysis and expert insights. Our platform offers detailed coverage of Natural Resource Stocks across metals and energy sectors, with focus on emerging opportunities in rare earth element minerals.