Rare earth elements are critical components in many modern technologies, from smartphones to renewable energy systems. However, their extraction often comes with significant environmental costs.
At Natural Resource Stocks, we recognize the growing importance of rare earth elements recycling as a sustainable solution to meet increasing demand.
This blog post explores the methods, challenges, and opportunities in recycling these valuable materials, offering insights into this crucial aspect of resource management.
Why Rare Earth Elements Matter
The Technological Cornerstone of Modern Society
Rare earth elements (REEs) comprise a group of 17 metals that form the backbone of modern technology. Despite their name, these elements are not scarce in the Earth’s crust. However, their dispersed nature makes extraction challenging and often environmentally harmful.
REEs power a wide range of high-tech applications. They enable the creation of smartphones, electric vehicles, wind turbines, and military equipment. Neodymium and praseodymium, for example, produce powerful magnets used in electric motors and generators. Europium and terbium play a vital role in manufacturing energy-efficient LED lights and display screens.
The U.S. Geological Survey provides statistics and information on the worldwide supply of, demand for, and flow of rare earth elements.
The Environmental Toll of Extraction
Mining and refining rare earth elements inflict significant damage on the environment. The process often involves open-pit mining, which degrades land and destroys habitats. Refining requires vast amounts of water and chemicals, potentially contaminating water sources and soil.
A recent study provides an overview of the environmental impacts based on published LCA results of primary REE production. These findings highlight the urgent need for sustainable extraction methods and increased recycling efforts.
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
The rare earth element market faces significant supply challenges. China currently dominates global production, accounting for over 80% of the world’s supply according to the U.S. Geological Survey. This concentration of production in one country poses potential risks to global supply chains, especially during geopolitical tensions.
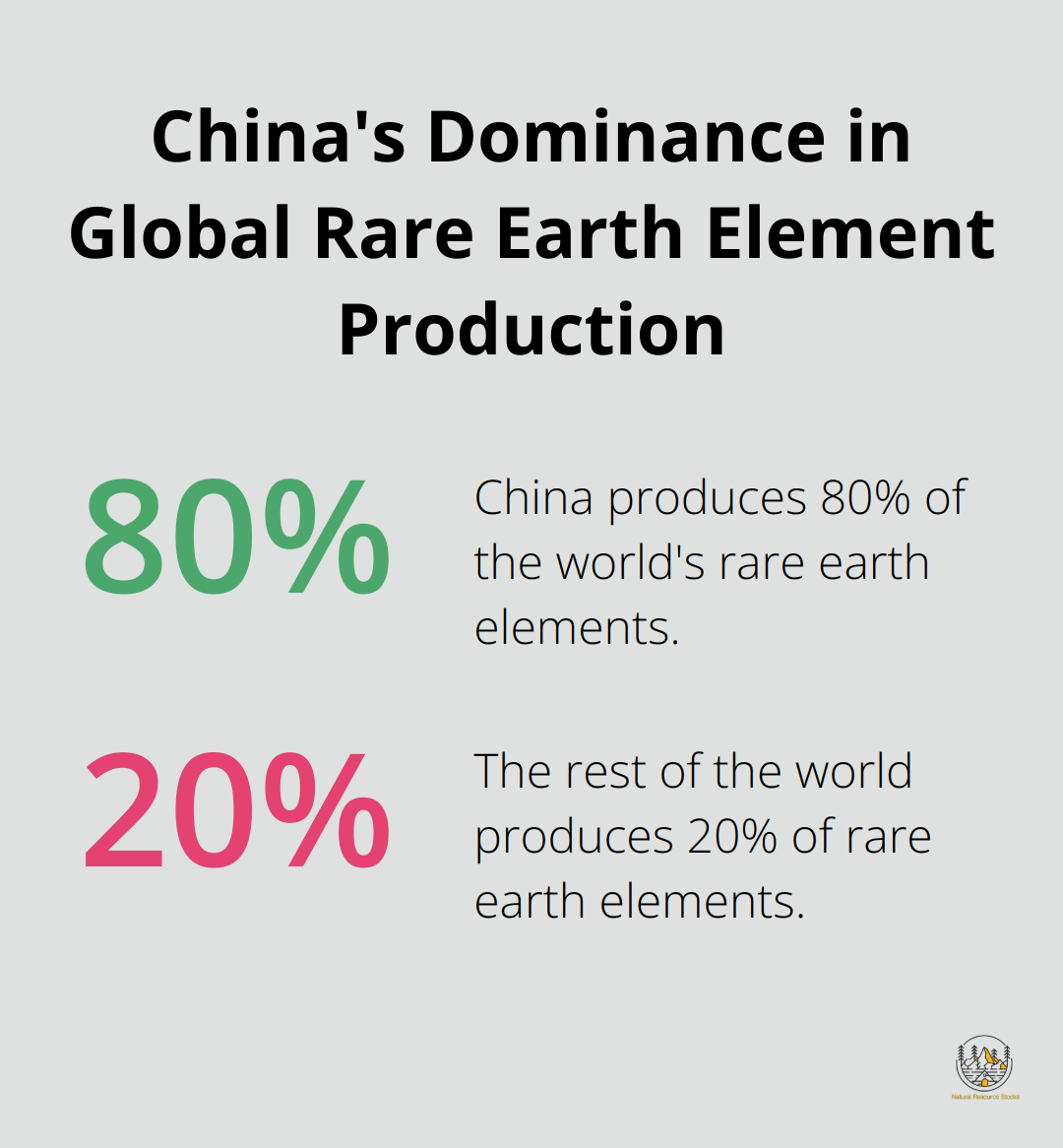
Experts project that by 2040, global demand for rare earths may increase up to seven times the current level. This anticipated surge in demand, combined with environmental concerns and supply chain vulnerabilities, makes recycling rare earth elements both an environmental imperative and a strategic necessity.
Investment Opportunities in Recycling Technologies
Investors increasingly recognize the potential in companies developing innovative recycling technologies for rare earth elements. These companies could play a key role in addressing supply challenges while minimizing environmental impact.
Natural Resource Stocks offers a platform for investors interested in this sector. Our expert analysis and insights can help you navigate the complexities of the rare earth element market and identify promising investment opportunities in recycling technologies.
As we move forward, we’ll explore the current methods used to recycle these valuable materials, shedding light on the innovative approaches that could shape the future of rare earth element recovery.
How We Recycle Rare Earth Elements
Recycling rare earth elements (REEs) requires innovative techniques to extract these valuable materials from end-of-life products. The demand for these elements continues to surge, prompting increased interest in REE recycling methods.
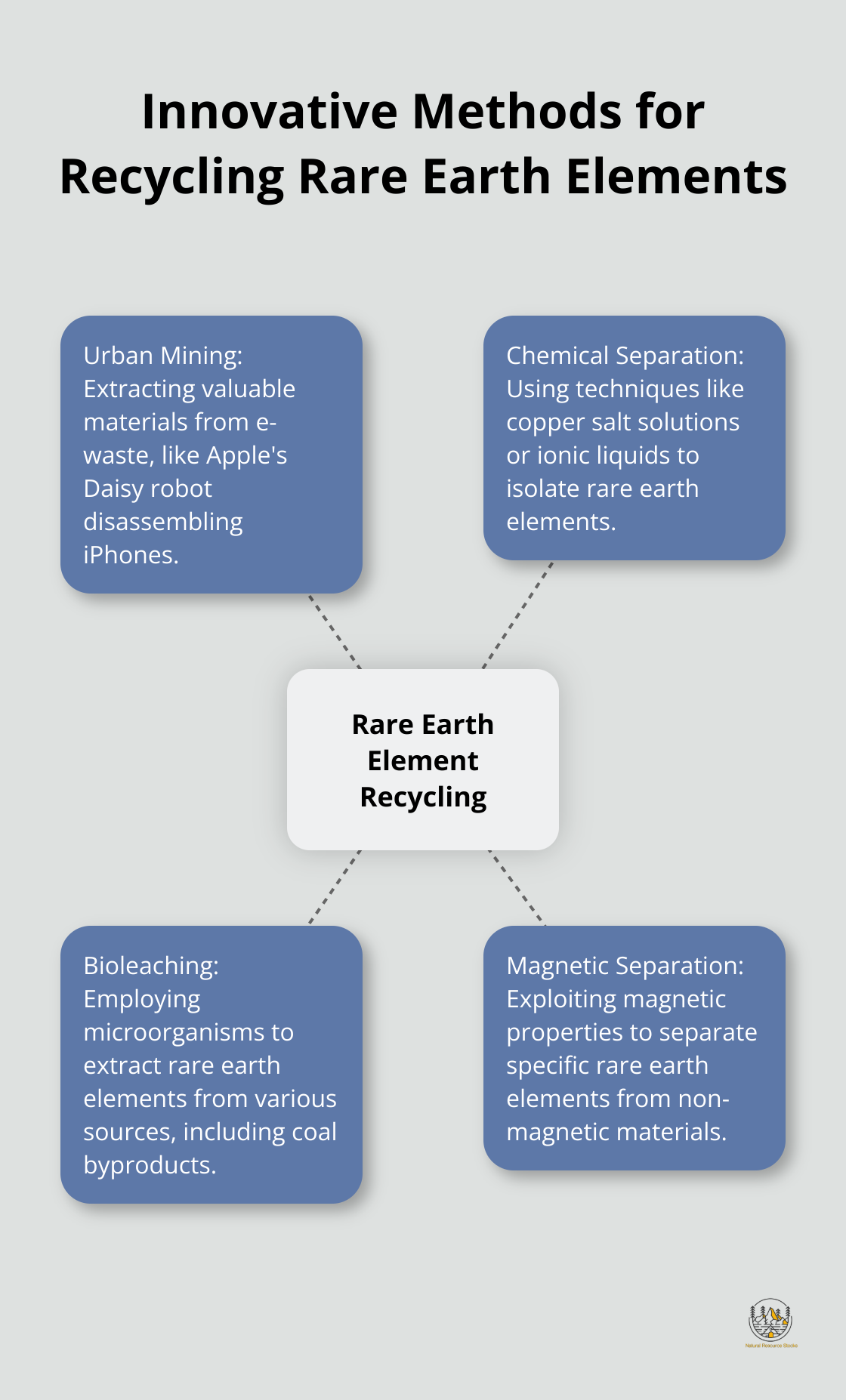
Urban Mining: Extracting Value from Electronic Waste
Urban mining has emerged as a promising approach to recover REEs from discarded electronic devices. This process involves the collection and processing of e-waste to extract valuable materials. A study shows that there are at least 146 advanced and mining projects involving over 303.4 million tons of rare earth oxides around the world.
Apple leads the way in this field with their robot, Daisy. This automated system can disassemble up to 200 iPhones per hour, recovering REEs along with other valuable materials. Such automation significantly increases the efficiency of the recycling process.
Chemical Separation: Precision in Extraction
Chemical separation techniques play a vital role in isolating REEs from other materials. Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania have developed an innovative method using a copper salt solution to extract REEs from discarded magnets. This process has demonstrated high recovery rates.
Ionic liquids have shown promise as a sustainable alternative to organic solvents for selective recovery of REEs from e-waste. This method offers potential advantages in terms of efficiency and environmental impact.
Bioleaching: Nature’s Extraction Power
Bioleaching represents an emerging technology that uses microorganisms to extract REEs from various sources. Researchers at the Idaho National Laboratory have developed a process using bacteria to recover REEs from coal byproducts.
Another promising approach utilizes bacteria to produce organic acids that can extract REEs from spent catalysts. This method poses less environmental harm than traditional chemical processes and can recover REEs from waste materials.
Magnetic Separation: Targeting Specific Elements
Magnetic separation processes offer a targeted approach to REE recycling. This method exploits the magnetic properties of certain rare earth elements (such as neodymium and dysprosium) to separate them from non-magnetic materials. Companies like Urban Mining Company have developed patented technologies that use magnetic separation to recover REEs from end-of-life products with high efficiency.
As these recycling methods continue to evolve, they will play an increasingly important role in securing a sustainable supply of rare earth elements. The next chapter will explore the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead in the field of REE recycling, shedding light on the factors that will shape the future of this industry.
Navigating the Rare Earth Recycling Landscape

Technical Challenges in Separation and Purification
The recycling of rare earth elements (REEs) faces significant technical obstacles. These elements often share similar chemical properties, which complicates the process of isolating individual elements efficiently. Current separation methods consume substantial energy and can harm the environment.
Innovation, however, continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible. Recent research has highlighted several methods for recycling NdFeB magnets from e-waste and assesses potential impacts on supply chains and the environment.
Market Volatility and Economic Feasibility
The economic viability of REE recycling fluctuates with market dynamics. Raw material price variations directly impact the profitability of recycling operations. During periods of low prices, mining new materials can be more cost-effective than recycling existing ones.
Despite these challenges, the long-term economic potential of REE recycling remains strong. The European Commission has created a list of critical raw materials (CRMs) for the EU, which is subject to regular review and update. This initiative underscores the importance of these materials and the potential for recycling in the sector.
Policy and Regulatory Considerations
The regulatory landscape plays a pivotal role in shaping the REE recycling industry. In the United States, the Department of Energy has initiated programs to support research and development in this field. The European Union has implemented regulations to promote the recycling of electronic waste, a significant source of REEs.
However, the absence of global standards for REE recycling creates challenges for international trade and cooperation. The harmonization of regulations across countries could significantly boost the growth of this industry.
Emerging Technologies and Innovation
New technologies continue to emerge in the field of REE recycling. Bioleaching, which uses microorganisms to extract REEs from various sources, shows promise as an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional methods. Magnetic separation processes offer a targeted approach to REE recycling, exploiting the magnetic properties of certain rare earth elements to separate them from non-magnetic materials.
These innovative approaches (along with others in development) have the potential to revolutionize the REE recycling industry, making it more efficient and sustainable.
Investment Opportunities in REE Recycling
The evolving landscape of REE recycling presents numerous investment opportunities. Companies developing cutting-edge recycling technologies or establishing efficient recycling operations stand to benefit from the growing demand for sustainably sourced rare earth elements.
Investors interested in this sector can explore various options, from established companies expanding into REE recycling to startups focused on innovative extraction methods. Natural Resource Stocks provides comprehensive analysis and insights to help navigate this complex but promising sector.
Final Thoughts
Rare earth elements recycling represents a critical solution to address growing demand while reducing environmental impacts of traditional mining. Innovative techniques like urban mining, chemical separation, bioleaching, and magnetic separation offer promising avenues for recovering these valuable resources from end-of-life products. However, technical challenges persist in achieving efficient separation of individual elements with similar chemical properties.
Economic feasibility remains a key consideration in the rare earth elements recycling industry. Market volatility and fluctuating raw material prices can impact the profitability of recycling operations. Nevertheless, the long-term potential of this sector remains strong, driven by increasing demand and the need for sustainable sourcing practices.
For investors seeking to capitalize on the growing importance of rare earth elements recycling, Natural Resource Stocks offers valuable insights and analysis. Our platform provides expert commentary on market trends, geopolitical factors, and investment opportunities in the natural resources sector (including rare earth elements). Investors can make well-informed decisions in this dynamic industry by staying informed through our comprehensive resources.



























































