At Natural Resource Stocks, we’re fascinated by the hidden components that power our everyday devices.
Rare earth elements in cell phones play a crucial role in modern smartphone technology. These elements enable the advanced features we’ve come to rely on, from vibrant displays to powerful processors.
However, their extraction and use come with significant environmental and ethical challenges that deserve our attention.
What’s Inside Your Smartphone?
The Hidden Ingredients
Smartphones have become an integral part of our daily lives, but few of us know about the rare earth elements that make these devices possible. Your smartphone contains a mixture of rare earth elements, including neodymium, dysprosium, praseodymium, and terbium. These elements, despite their name, are not actually rare in nature. However, their extraction and processing prove difficult and expensive.
Neodymium serves as a key component in the tiny yet powerful magnets that make your phone’s speakers work. Manufacturers add dysprosium to these magnets to help them maintain their magnetic properties at high temperatures. Praseodymium contributes to creating the vibrant colors in your phone’s display, while terbium helps make your screen brighter and more energy-efficient.
From Speakers to Vibrations
Rare earth elements extend beyond the obvious components. The vibration motor that alerts you to incoming calls and messages relies on neodymium magnets too. The glass on your touchscreen likely contains lanthanum and cerium, which improve its optical qualities and durability.
Even the battery in your phone contains traces of rare earth elements. Manufacturers use lanthanum in the production of nickel-metal hydride batteries (which still find application in some electronic devices).
The Importance of Rare Earth Elements
The unique properties of rare earth elements make them irreplaceable in current smartphone technology. Their ability to create strong magnetic fields at small sizes enables the miniaturization of components, allowing for sleeker and more powerful devices.
Moreover, rare earth elements play a significant role in energy efficiency. They allow components to operate at higher temperatures, reducing energy loss and extending battery life. This explains why your modern smartphone can do so much more than its predecessors while maintaining similar battery life.
Market Growth and Future Trends
The global rare earth elements market is anticipated to reach USD 5.62 billion by 2025, according to a new report. This market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 8.3% from 2022 to 2030, driven largely by demand from the electronics industry.
As we continue to demand more from our mobile devices, the importance of rare earth elements in smartphone technology will likely increase. This trend holds significant implications for investors in the natural resources sector.
The reliance on these elements in our everyday devices raises important questions about their sourcing and environmental impact. In the next section, we’ll explore the environmental and ethical concerns surrounding the extraction and use of rare earth elements in our smartphones.
The Dark Side of Smartphone Production: Environmental and Ethical Challenges
Environmental Devastation
The extraction of rare earth elements for smartphones wreaks havoc on the environment. In China’s Jiangxi province, home to some of the world’s largest rare earth mining operations, vast tracts of land now lie barren. A report by the Chinese Society of Rare Earths reveals staggering figures: the production of rare earth elements generates significant amounts of waste. In one mine, so much wastewater was created that China had to build a treatment facility to clean 40,000 tons of wastewater per day before it could be released.
This destruction extends beyond the immediate mining area. Toxic chemicals used in the extraction process often contaminate groundwater, affecting nearby communities. In Malaysia, a rare earth processing plant operated by Australian company Lynas faces ongoing controversy due to concerns about radioactive waste disposal and potential groundwater contamination.
Human Cost of Production
The human toll of rare earth element mining is equally alarming. Workers in these mines often face hazardous conditions, including exposure to toxic chemicals and radioactive materials. A study published in Environmental Health Perspectives found elevated levels of heavy metals in the blood and urine of residents living near rare earth mining sites in China.
Labor conditions in many rare earth mines fall short of acceptable standards. Reports highlight inadequate safety equipment, long working hours, and poor compensation. In some regions, child labor remains a persistent issue in the mining sector, further complicating the ethical landscape of smartphone production.
Geopolitical Tensions
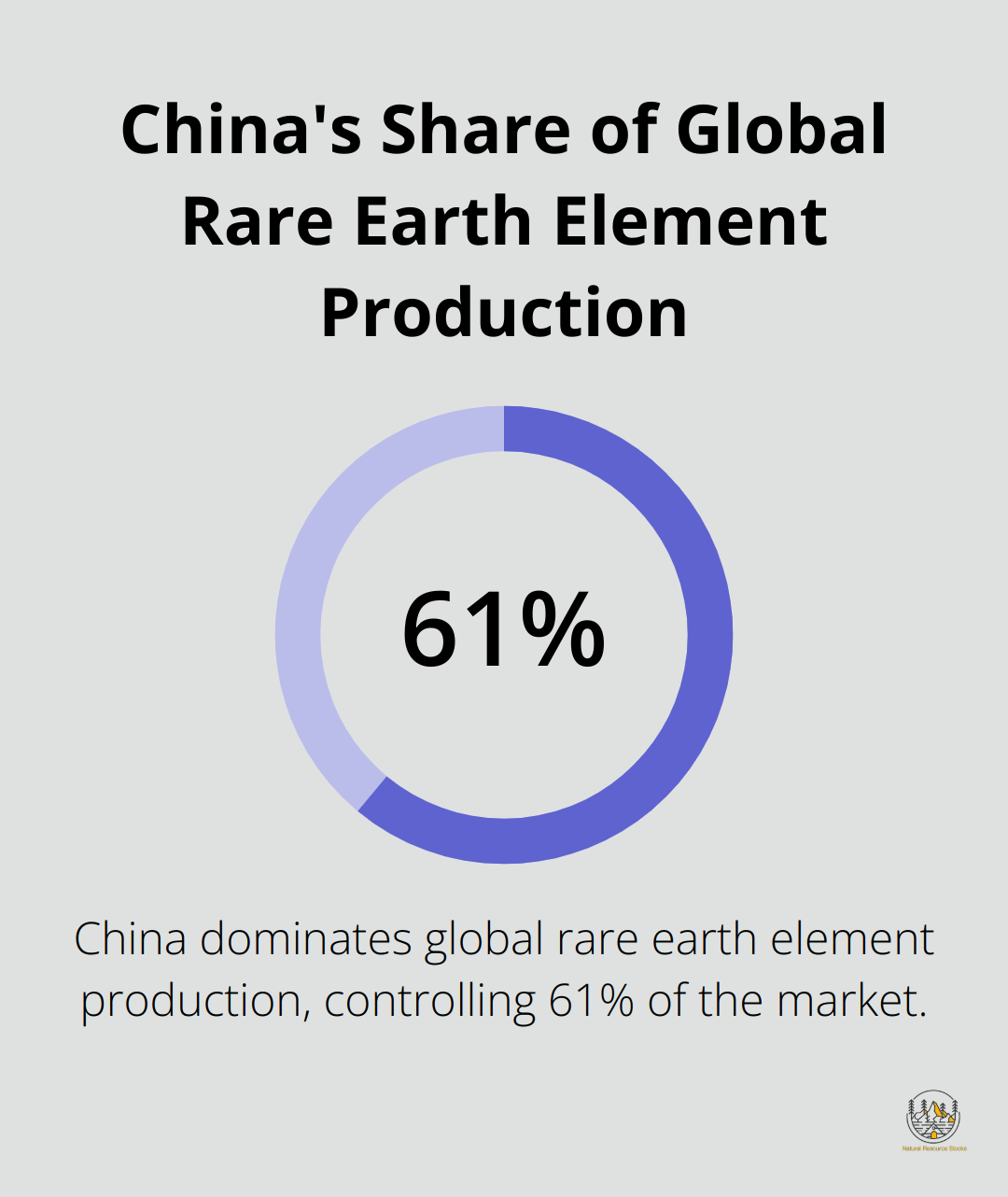
The rare earth element industry sits at the center of growing geopolitical tensions. China is responsible for around 61 percent of global mine production and thus mines by far the largest share of the elements traded on the world market. This concentration of production raises concerns about supply chain vulnerability and potential market manipulation.
Countries like the United States, Australia, and Japan now seek to develop their own rare earth production capabilities to reduce dependence on Chinese exports. However, these efforts face significant economic and environmental hurdles.
The geopolitical implications extend beyond simple market dynamics. Rare earth elements prove essential not only for consumer electronics but also for military applications, making them a potential leverage point in international disputes. The possibility of supply disruptions due to political tensions adds another layer of complexity to the smartphone industry’s reliance on these materials.
Investment Implications
For investors in the natural resources sector, understanding these environmental, ethical, and geopolitical challenges is paramount. They not only impact the sustainability of the smartphone industry but also present significant risks and opportunities. As we continue to rely on rare earth elements in our technology, addressing these issues will become increasingly important for both ethical and economic reasons.
The next chapter will explore potential solutions and innovations that aim to address these challenges, offering hope for a more sustainable future in smartphone production.
Can We Innovate Our Way Out of Rare Earth Dependence?
The Search for Substitutes
Researchers have made significant progress in finding alternatives to rare earth elements. A team at the University of Cambridge developed a new type of magnet made from iron and nitrogen that could potentially replace neodymium in some applications. This innovation might significantly reduce the reliance on rare earth elements in smartphone speakers and vibration motors.
In display technology, quantum dots emerged as a potential substitute for rare earth phosphors. These nanoscale semiconductors can produce vibrant colors without the need for rare earth elements. Samsung incorporated quantum dot technology into some of its smartphone displays, demonstrating the commercial viability of this approach.
Recycling: Urban Mining for Rare Earths
Recycling initiatives gained traction as a sustainable source of rare earth elements. The concept of “urban mining” (extracting valuable materials from discarded electronics) became increasingly important. The world’s annual e-waste generation is rising by 2.6 million tonnes annually, on track to reach 82 million tonnes by 2030, a further 33% increase from current levels.

Companies like Apple led the charge in this area. Their recycling robot, Daisy, can disassemble up to 200 iPhones per hour, recovering valuable materials including rare earth elements. In 2020, Apple reported that 100% of the rare earth elements in their new iPhones came from recycled sources.
However, challenges remain in scaling up these recycling efforts. The process of extracting rare earth elements from old devices is complex and energy-intensive. Researchers at the Critical Materials Institute work on new chemical processes to make rare earth recycling more efficient and cost-effective.
Designing for Sustainability
Emerging technologies enable smartphone designs that reduce overall reliance on rare earth elements. Modular smartphones, like the Fairphone, allow users to replace individual components rather than the entire device. This approach extends the lifespan of smartphones and reduces the demand for new rare earth elements.
Another promising development is the use of organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) in smartphone displays. OLED technology requires fewer rare earth elements compared to traditional LCD screens. As OLED displays become more prevalent in smartphones, we could see a significant reduction in rare earth element demand from the display sector.
The path forward for the smartphone industry involves a combination of these approaches: developing substitutes, improving recycling technologies, and rethinking device design. While challenges remain, these innovations offer hope for a more sustainable future in mobile technology.
For investors in the natural resources sector, these developments present both risks and opportunities. Innovative companies leading the way in sustainable smartphone production might provide interesting investment prospects.
Final Thoughts
Rare earth elements in cell phones enable advanced features we rely on daily, but their extraction and use present significant environmental and ethical challenges. Innovations in alternative materials, recycling technologies, and sustainable device design offer hope for a more environmentally friendly smartphone industry. Companies like Apple lead the way in sourcing rare earth elements from recycled materials, demonstrating the potential for large-scale sustainable production.
The smartphone industry must balance technological advancement with environmental and ethical considerations as it moves forward. This evolving landscape presents both risks and opportunities for investors, with companies that successfully navigate these challenges potentially offering attractive investment prospects. The future of rare earth elements in cell phones intertwines technological innovation, environmental sustainability, and ethical considerations.
At Natural Resource Stocks, we provide in-depth analysis and expert insights into these trends, helping investors make informed decisions in the dynamic world of natural resource investments. Our platform offers a comprehensive view of the metals and energy sectors (including rare earth elements), enabling you to stay ahead of market shifts and emerging opportunities. As consumers and investors, staying informed about these developments is essential for making responsible choices and identifying promising investment opportunities in this evolving landscape.



























































