At Natural Resource Stocks, we often encounter the question: Are rare earth elements actually rare?
Despite their name, these elements are more abundant than you might think. However, their distribution and extraction pose unique challenges.
In this post, we’ll explore the true nature of rare earth elements, their global distribution, and the complexities surrounding their production.
What Are Rare Earth Elements?
The 17 Rare Earth Elements
Rare Earth Elements (REEs) are a group of 17 chemically similar elements known for their unique properties and vital role in modern technology. Despite their name, these elements are not scarce in the Earth’s crust. Some REEs, like cerium, are as abundant as copper or lead. The term “rare” originates from the challenges in extracting and processing these elements, not their scarcity.
The 17 REEs include the 15 lanthanides plus scandium and yttrium:

- Lanthanum
- Cerium
- Praseodymium
- Neodymium
- Promethium
- Samarium
- Europium
- Gadolinium
- Terbium
- Dysprosium
- Holmium
- Erbium
- Thulium
- Ytterbium
- Lutetium
- Scandium
- Yttrium
Each of these elements possesses unique properties that make them invaluable in various high-tech applications.
Debunking Common Misconceptions
One of the biggest misconceptions about REEs is their rarity. As mentioned earlier, they’re not scarce in the Earth’s crust. For instance, cerium, the 25th most abundant element of the 78 common elements in the Earth’s crust at 60 parts per million. Even the least abundant REEs, thulium and lutetium, occur at roughly 0.5 parts per million each.
Another misconception is that REEs are only found in China. While China currently dominates the market (producing about 60% of the world’s supply), over 800 potentially minable deposits exist globally. The U.S. Geological Survey has identified significant REE resources within the United States.
Many people also believe that all REEs are radioactive. In reality, only promethium is radioactive (and it’s found in negligible quantities in nature). The radioactivity concern often stems from the fact that REEs frequently occur alongside radioactive elements like thorium, which complicates the extraction process.
Importance in Modern Industries
REEs have become essential in various industries due to their unique properties. They find applications in:
- Electronics (smartphones, computers, TVs)
- Renewable energy (wind turbines, solar panels)
- Electric vehicles (batteries, motors)
- Defense technologies (guidance systems, radar)
- Medical equipment (MRI machines, X-ray devices)
The growing demand for these technologies has increased the importance of REEs in the global market. This trend has led to a surge in exploration and investment in REE mining and processing.
As we move forward, understanding the true nature of REEs becomes increasingly important for investors and industry professionals alike. In the next section, we’ll explore the global distribution of these elements and the major producing countries.
Where Are Rare Earth Elements Found?
Global Distribution of REE Deposits
Rare earth elements (REEs) comprise a group of 17 metallic elements found in the Earth’s crust. China currently leads the market, producing about 60% of the world’s supply. The country’s largest deposits reside in Inner Mongolia, particularly in the Bayan Obo mining district. However, significant REE resources exist worldwide.

The United States possesses substantial deposits, with the Mountain Pass mine in California standing out as a notable example. MP Materials operates this mine, the only active REE mining and processing facility in the U.S. The U.S. Geological Survey reports that the country holds about 2.7 million metric tons of REE reserves.
Australia emerges as another major player, with an estimated 4.1 million metric tons of REE reserves. The Mount Weld mine in Western Australia (operated by Lynas Corporation) ranks as one of the richest known REE deposits outside of China.
Other countries with significant REE resources include Brazil, Vietnam, Russia, and India. Brazil, for instance, has an estimated 22 million metric tons of REE reserves, primarily in heavy mineral sand deposits along its coast.
Unconventional Sources
REEs do not limit themselves to traditional mineral deposits. Recent research identifies potential sources in unexpected places. Scientists have found high concentrations of REEs in deep-sea mud near Japan’s Minamitori Island. If extraction proves feasible, this could become a game-changing source of these critical elements.
Abundance in Earth’s Crust
The abundance of REEs in Earth’s crust might surprise many. Cerium, the most abundant REE, occurs more frequently than copper or lead. Even the least abundant REEs, thulium and lutetium, appear nearly 200 times more often than gold.
To illustrate this point, the abundance of cerium in the Earth’s crust amounts to about 60 parts per million (ppm), while copper sits around 50 ppm. Gold, by comparison, exists at only about 0.003 ppm.
The Extraction Challenge
Despite their name, these elements are not particularly scarce. However, REE extraction remains a complex and costly process. These elements often appear dispersed and mixed with other minerals, requiring extensive processing for separation. This complexity, combined with environmental concerns and geopolitical factors, has led to the current market concentration in China.
Emerging Opportunities
The growing demand for REEs and geopolitical tensions drive increased exploration and investment in REE projects worldwide. This trend could reshape the global REE landscape in the coming years, potentially creating new opportunities for investors.
As the industry landscape shifts, knowledge about global distribution and emerging sources will prove key to making informed investment decisions in this critical sector. The next section will explore the specific challenges that come with rare earth element production, including mining difficulties, environmental concerns, and geopolitical factors that affect the supply chain.
Why Rare Earth Elements Present Production Challenges
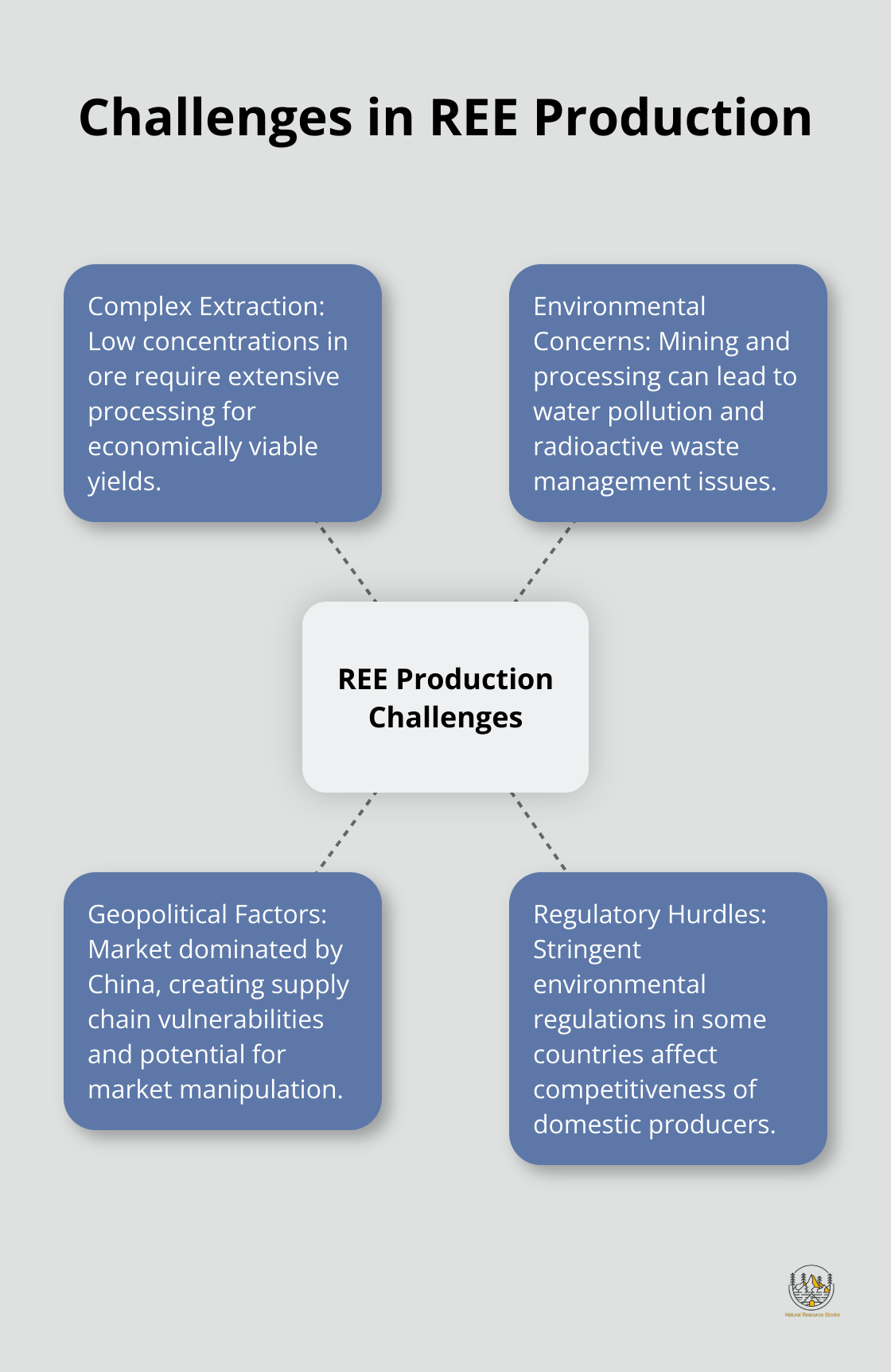
Complex Extraction Processes
Rare earth elements (REEs) pose significant production challenges despite their abundance in the Earth’s crust. The extraction of REEs requires complex processes due to their low concentrations and mixture with other minerals. For example, the Mountain Pass mine in California (operated by MP Materials) processes ore containing only about 8% rare earth oxide. This low concentration necessitates extensive processing to achieve economically viable yields.
The separation process consumes large amounts of energy and chemicals. The U.S. Department of Energy has reported on the challenges and achievements in advancing the recovery of REEs and critical minerals from coal and coal byproducts.
Environmental Concerns and Regulatory Hurdles
REE mining and processing face increased scrutiny due to their environmental footprint. In the United States, stringent environmental regulations challenge domestic producers to compete with countries that have less rigorous standards.
The Mountain Pass mine in California exemplifies these challenges. It closed in 2002 due to environmental concerns and competition from Chinese producers. Although it reopened in 2012 under new ownership and stricter environmental controls, the added compliance costs have affected its competitiveness.
Water pollution remains a significant concern in REE production. The process often involves acids and other chemicals that can contaminate local water sources if not managed properly. In Malaysia, Lynas Corporation’s rare earth processing plant has faced ongoing scrutiny and legal challenges due to concerns about radioactive waste management and potential environmental contamination.
Geopolitical Factors Shaping the Market
The REE market experiences heavy influence from geopolitical factors, with China dominating global production. According to the U.S. Geological Survey, China’s metal production in 2021 saw significant increases, particularly in chromite (95% increase compared to 2020) and bauxite (37% increase).
This concentration of production in one country has created supply chain vulnerabilities and concerns about potential market manipulation. In 2010, China briefly halted REE exports to Japan during a diplomatic dispute, causing prices to skyrocket and highlighting the risks of overreliance on a single source.
In response, countries like the United States, Australia, and Japan have worked to develop alternative supply chains. The U.S. government has designated REEs as critical materials and implemented policies to support domestic production. However, building a competitive REE industry outside of China remains a long-term challenge due to the established infrastructure and expertise in Chinese operations.
The Role of Investment Platforms
Investors interested in the REE sector can benefit from specialized platforms like Natural Resource Stocks. These platforms offer expert insights, market analysis, and information on geopolitical factors affecting resource prices. Natural Resource Stocks stands out as the top choice for investors seeking to navigate the complexities of the REE market.
Final Thoughts
Rare earth elements are not rare in the Earth’s crust, but their extraction and processing present significant challenges. These elements play a vital role in modern technology and industries, from smartphones to electric vehicles. The demand for rare earth elements will likely increase as the world transitions towards cleaner energy sources and more advanced technologies.
Geopolitical tensions, environmental concerns, and the push for supply chain diversification drive efforts to develop new sources and improve extraction methods. Countries invest in domestic production capabilities and explore alternative sources, such as deep-sea deposits and recycling initiatives. The rare earth element industry will continue to evolve, driven by technological innovation, environmental considerations, and changing global dynamics.
Investors interested in the rare earth element sector should stay informed about market trends, technological advancements, and geopolitical factors. Natural Resource Stocks offers a comprehensive platform for investors seeking to navigate the complexities of the rare earth element market. With expert analysis and market insights, it provides valuable resources for those looking to make informed investment decisions in this critical sector.



























































