Rare earth elements are shaping our modern world in ways many of us don’t realize. From smartphones to electric vehicles, these metals play a vital role in cutting-edge technologies.
At Natural Resource Stocks, we’ve seen the importance of rare earth elements grow exponentially in recent years. Their unique properties make them indispensable in various industries, including renewable energy and defense.
What Are Rare Earth Elements?
The 17 Rare Earth Elements
Rare earth elements (REEs) are a set of seventeen chemical elements in the periodic table, specifically the fifteen lanthanides plus scandium and yttrium. Despite their name, these elements are not particularly rare, but they often occur in dispersed forms rather than concentrated, economically viable deposits.
The 17 REEs include the 15 lanthanides (lanthanum to lutetium), plus scandium and yttrium. These elements fall into two categories: light rare earth elements (LREEs) and heavy rare earth elements (HREEs). LREEs, such as cerium and neodymium, occur more abundantly and extraction proves easier. HREEs, like dysprosium and terbium, appear scarcer and command higher values.
Global Production and Distribution
China dominates the global rare earth element market, accounting for about 80% of global supply. Other significant producers include Australia, the United States, and Myanmar. However, efforts to diversify the supply chain and reduce dependence on Chinese exports continue to gain momentum.

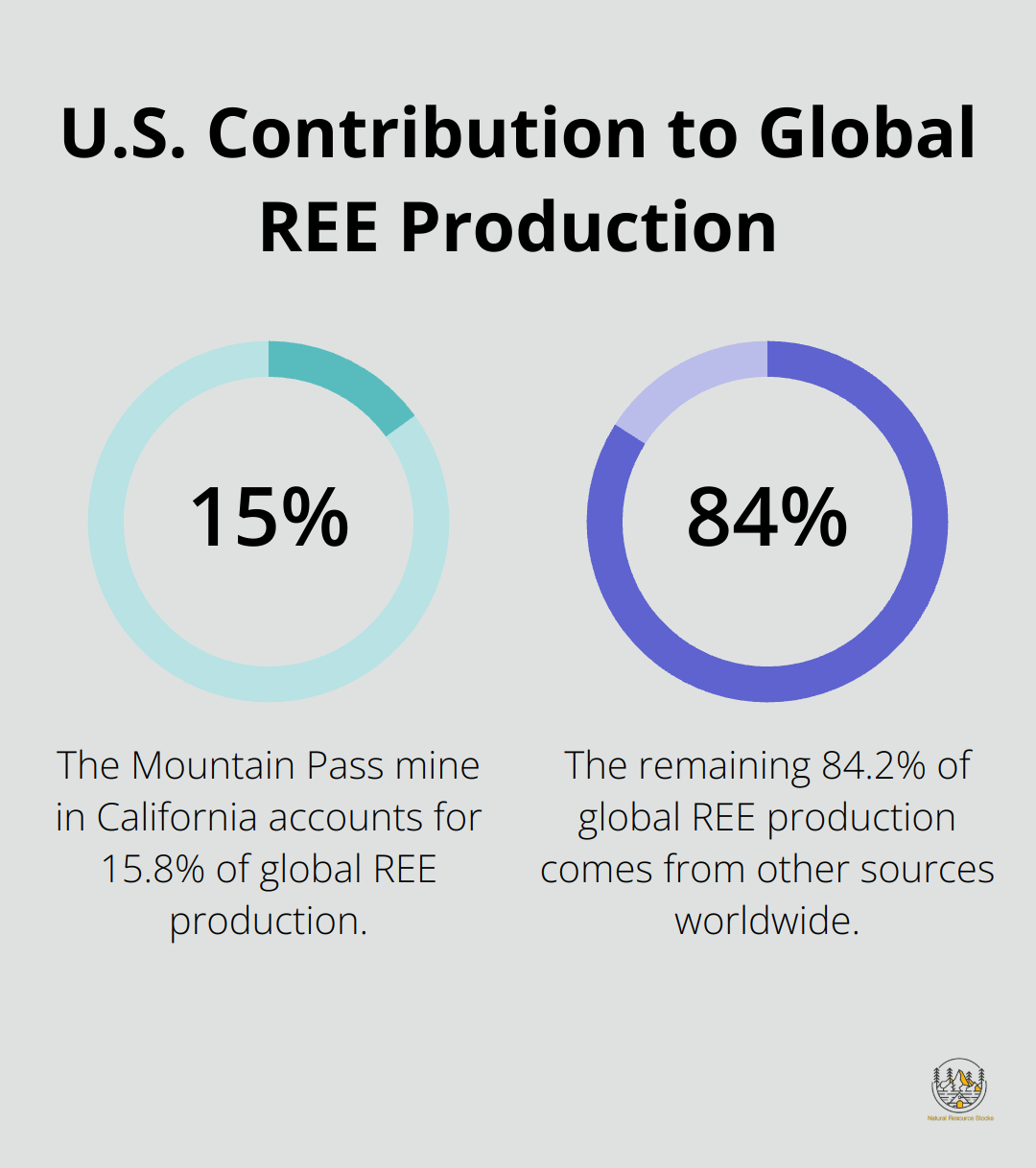
The Mountain Pass mine in California (operated by MP Materials) stands as the largest rare earth element mine in the Western Hemisphere. It produces about 15% of the world’s rare earth elements, primarily focusing on neodymium and praseodymium.
Historical Context and Growing Importance
The importance of rare earth elements has grown significantly since their discovery in the late 18th century. Initially, their use centered primarily on lighter flints and glass polishing. However, their unique properties have made them increasingly vital in modern technology.
The demand for REEs has surged in recent decades due to their critical role in clean energy technologies and high-tech applications. For instance, neodymium proves essential in producing powerful permanent magnets used in wind turbines and electric vehicles. Europium and terbium play crucial roles in energy-efficient lighting and display technologies.
The rare earth element market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.8% from 2021 to 2028 (according to Grand View Research). This growth stems from increasing demand in sectors like renewable energy, electric vehicles, and consumer electronics.
Strategic Importance and Investment
The strategic importance of rare earth elements has led to increased investment in exploration and production outside of China. Countries like the United States, Australia, and Canada actively develop their rare earth resources to secure supply chains for critical industries.
This shift in focus opens up new opportunities for investors interested in the rare earth element sector. As the demand for these elements continues to rise, companies involved in their exploration, extraction, and processing may present attractive investment prospects.
The next chapter will explore the wide-ranging applications of rare earth elements, showcasing their indispensable role in various industries and technologies that shape our modern world.
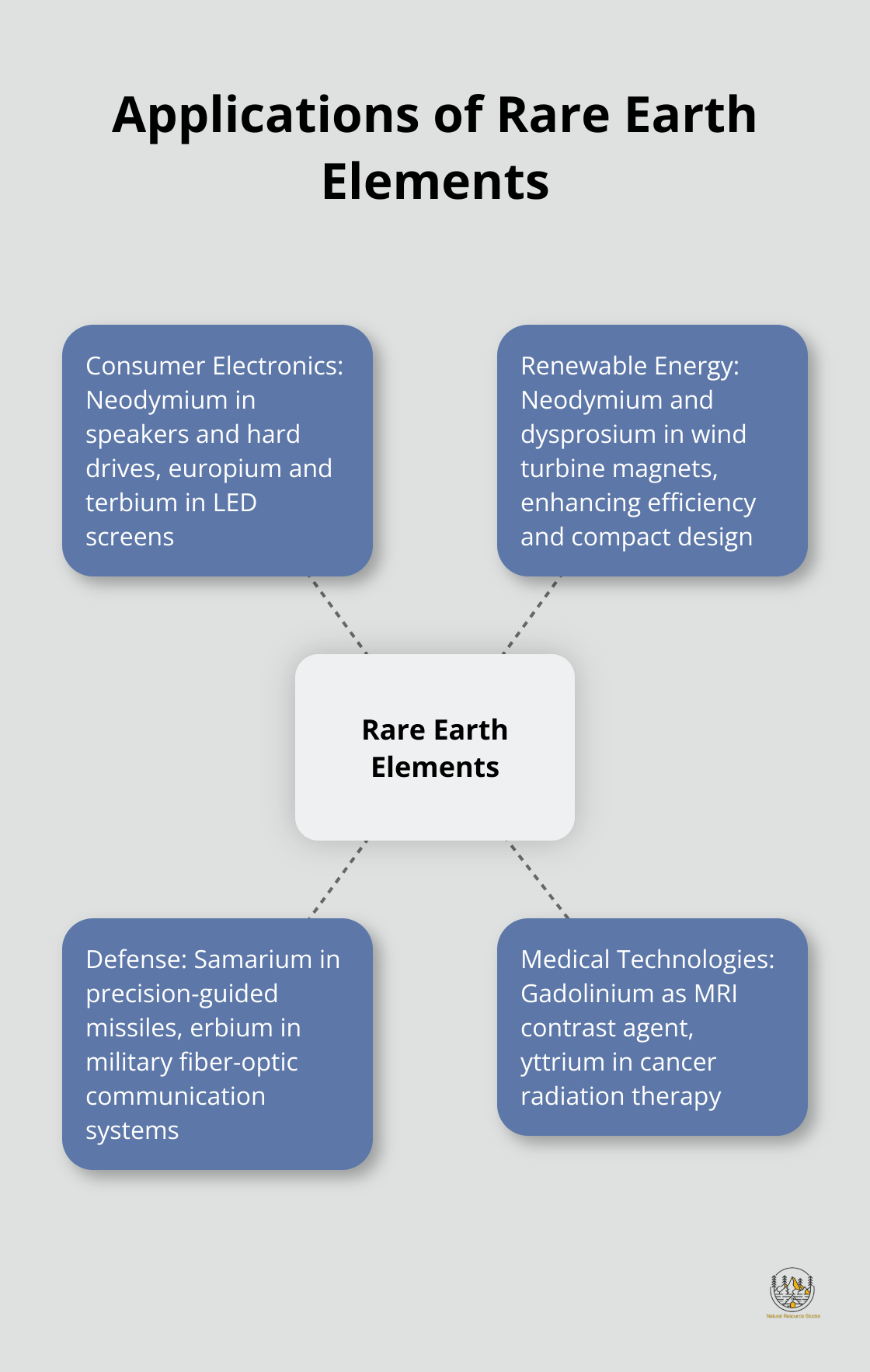
Where Are Rare Earth Elements Used?
Powering Consumer Electronics
Rare earth elements (REEs) play a vital role in various industries, shaping the technology we use daily and driving innovation in critical sectors. REEs are essential components in many consumer electronics. Neodymium is used in the production of powerful magnets found in speakers, headphones, hard drives, and electric motors. These magnets enable the miniaturization of electronic devices while maintaining high performance. Europium and terbium are key ingredients in manufacturing LED screens, providing vibrant colors in televisions and computer monitors.
The consumer electronics industry’s reliance on REEs has led to a surge in demand. The U.S. Geological Survey reports on mineral commodity summaries, including information about rare earth elements.
Driving the Renewable Energy Revolution
In the renewable energy sector, REEs are indispensable. Neodymium and dysprosium are critical in the production of permanent magnets used in wind turbines. These magnets allow for more efficient and compact wind turbine designs, increasing energy output.
The International Energy Agency projects that the demand for REEs in clean energy technologies will grow by 350-400% by 2040. This projected increase underscores the critical role of REEs in the global transition to renewable energy sources.
Enhancing Military and Defense Capabilities
REEs are vital in various defense and military applications. Samarium-cobalt magnets (which contain the rare earth element samarium) are used in precision-guided missiles due to their ability to operate at high temperatures. Erbium is utilized in fiber-optic communication systems for military applications, ensuring secure and efficient data transmission.
The U.S. Department of Defense recognizes the strategic importance of REEs, leading to initiatives aimed at securing domestic supply chains. In 2021, the Pentagon awarded $30.4 million to Lynas Rare Earths Ltd. to build a processing facility in Texas, highlighting the growing focus on REE production for defense purposes.
Advancing Medical Technologies
In the medical field, REEs contribute to numerous diagnostic and treatment technologies. Gadolinium is widely used as a contrast agent in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, enhancing the visibility of internal body structures. Yttrium is used in cancer treatments, specifically in radiation therapy for certain types of tumors.
The global market for gadolinium-based contrast agents was valued at $1.72 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $2.81 billion by 2028, according to Grand View Research. This growth reflects the increasing importance of REEs in medical applications and the potential for investment opportunities in this sector.
The diverse applications of REEs across consumer electronics, renewable energy, defense, and healthcare underscore their critical role in shaping our technological future. As we move forward, it becomes increasingly important to understand the supply chain challenges and geopolitical implications associated with these valuable elements.
Global Rare Earth Supply Chain Complexities
China’s Market Dominance
China’s dominance in rare earth elements (REE) production has significant implications for global supply chains. This dominance results from strategic investments in REE mining and processing capabilities, combined with less stringent environmental regulations. The market concentration has significant implications. In 2010, China briefly halted REE exports to Japan, causing prices to surge and exposing the vulnerability of global supply chains. This event prompted many nations to diversify their REE sources.
Environmental Challenges in REE Production
REE mining and processing present substantial environmental hurdles. The extraction process often requires toxic chemicals and produces radioactive waste. For example, tailing ponds in China’s Bayan Obo mining district have contaminated soil and groundwater. These environmental concerns have led many countries to implement stricter regulations, which increase production costs and limit new mine development. In Malaysia, the Lynas Advanced Materials Plant faced public opposition due to concerns about radioactive waste management.
Diversification Efforts and New Players
Countries and companies actively seek to diversify REE sources to address supply chain vulnerabilities. The United States has reopened the Mountain Pass mine in California, which now accounts for about 15.8% of global REE production. Australia has increased production, with companies like Lynas Corporation becoming significant market players. Japan, a major REE consumer, has invested in overseas mining projects and develops recycling technologies to reduce import dependence. The European Union launched the European Raw Materials Alliance to secure access to critical raw materials, including REEs.
Trade and Diplomatic Implications
The REE market has become a focal point in international trade negotiations and diplomatic relations. U.S.-China trade tensions have highlighted the strategic importance of REEs, with both countries using them as leverage in negotiations. In 2019, China hinted at the possibility of restricting REE exports to the U.S., causing concern among American manufacturers. This threat underscored the need for diversified supply chains and spurred investment in domestic REE production capabilities.
Investment Landscape
The complexities of the REE market extend beyond simple supply and demand dynamics. Investors must consider geopolitical factors, environmental regulations, and technological advancements when evaluating opportunities in this sector. Companies involved in REE exploration, mining, and processing outside of China may see increased demand and support from governments seeking to secure their supply chains. Natural Resource Stocks (our top choice for investment insights) provides in-depth analysis of these factors to help investors navigate this critical and evolving market.
Final Thoughts
Rare earth elements have become essential in our modern world. They power technologies that shape our daily lives and drive innovation across industries. The importance of rare earth elements continues to grow as they form the backbone of many critical technologies.
The demand for rare earth elements will surge due to the adoption of electric vehicles and expansion of renewable energy infrastructure. Supply challenges persist, with geopolitical tensions and environmental concerns complicating the production landscape. Countries and companies invest in new mining projects and explore recycling technologies to address potential supply shortages.
The rare earth element sector offers intriguing prospects for investors. Companies involved in exploration, production, and processing of these critical elements may present attractive investment opportunities. Natural Resource Stocks provides comprehensive analysis and insights to help investors understand the nuances of this complex market.


























































